
Packaging Paper Faces Weaker Demand as Consumption Is Under Pressure
Intro: At the current stage, the demand for packaging paper was lackluster, and market participants reflected that it was mainly due to the sloppy consumption. From a macro perspective, the domestic consumption in China faced several challenges including the decrease in residents’ income, the deleveraging of the household sector as well as imported inflation. The downward pressure on consumption growth in China may affect the demand for packaging paper in later stages.
During the talks with participants in the packaging paper industry recently, most of them have shown some concerns over the performance of domestic consumption. Some suggested the orders dropped by a lot due to tepid end-demand lately. With the deceleration of consumption, the corrugated paper monthly average price also went down in March.
In March, the consumption and demand for consumables decelerated mainly due to the restrictions in some regions since late March. According to data from the NBS, the total retail sales of social consumables rose by 3.3% Y-O-Y in Q1, but it was apparently lower than the average growth of 6.7% in January and February mainly because of the -3.5% Y-O-Y decrease in March.
The influence of consumption growth on packaging paper prices has increased since 2020
Based on the monthly average corrugated paper price and the total retail sales of consumer goods, the two showed relatively weak co-movement before 2020. The growth rate of total retail sales of social consumer goods went down in general, while the corrugated paper market price was relatively volatile.
After 2020, with the recovery of domestic consumption, the corrugated paper price was also supported. But since April 2021, the growth rate of the total sales of social consumer goods has entered another downward slope. Although the corrugated paper price went up in 2021 supported by cost and export factors, the downward pressure from deceleration in consumption growth had also become prominent. From November of 2021, with more sluggish demand prospective in the Spring Festival holiday, the corrugated paper price also went downwards in general.
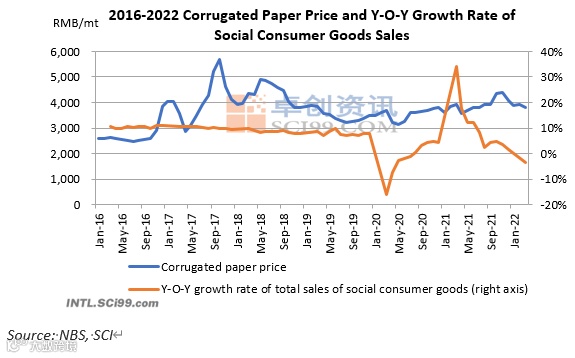
Entering 2022, with higher pressure from export growth, the influence of domestic consumption on packaging paper price trend became more apparent, and market participants were still cautious about the future consumption prospect. The following analysis will be done from three major aspects.
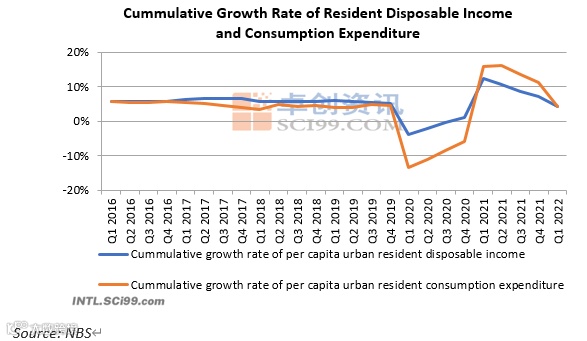
1. The growth rate of disposable income and expenditure of urban residents declined.
According to the NBS, in Q1 2022, the per capita average disposable income of urban residents rose by 5.4% Y-O-Y, and the per capita average expenditure rose by 5.7% Y-O-Y, which were apparently lower than the previous readings of 8.1% and 12.2%. Science the turning points in Q2 and Q3 of 2021, the downward trend has intensified. In the meantime, the unemployment rate of urban residents reached 5.8%, up 0.3% M-O-M, which is the second-highest level in history.
With the increase in the unemployment rate, spending and consumption will slow down, and there will be limited support for consumption recovery in later stages.
2. The household sector has entered a deleveraging stage
Based on the leverage ratio published by the National Institution for Finance and Development, from 2019 to 2020, the leverage ratio of the household had been rising constantly. In Q1 of 2009, the leverage ratio was 19%, but it had reached 62.2% at the end of 2020. However, in 2021, the leverage ratio stop growing, and by the end of the year, the leverage ratio stayed at 62.2%. With the real estate industry in China entering a recessive cycle, residents’ willingness of purchasing properties decreased. Besides, the household entered a deleveraging stage in 2022, which might further curb consumption.

3. Pressure from imported inflation to increase.
Based on the CPI in China and the RMB-USD exchange rate, as the depreciation pressure of the RMB exchange rate increased, the domestic inflation pressure also mounted. The depreciation of the RMB means higher import costs for China and the exposure to the risk of imported inflation.

Entering March, the pressure of depreciation in the RMB-USD exchange rate continued to mount. As of April 24, the central parity rate of the RMB-USD exchange rate has dropped to 6.5, down 3.17% from the highest point of the year. The commodity market hovered at highs due to supply chain cloggings worldwide. If the RMB exchange rate continues to depreciate, China will face mounting inflation pressure, which will also affect domestic consumption.
On the whole, consumption in China still faces pressure from multiple aspects, and if the growth in consumer goods sales decelerates in the future, the marginal downward pressure on packaging demand in China will also increase.
All information provided by SCI is for reference only, which shall not be reproduced without permission.
Please click "Read more" for the full article.



