
【财新网】(记者 张娱)受科技投入和资本投入下降影响,2018年5月万事达卡财新BBD中国新经济指数(NEI)微降。
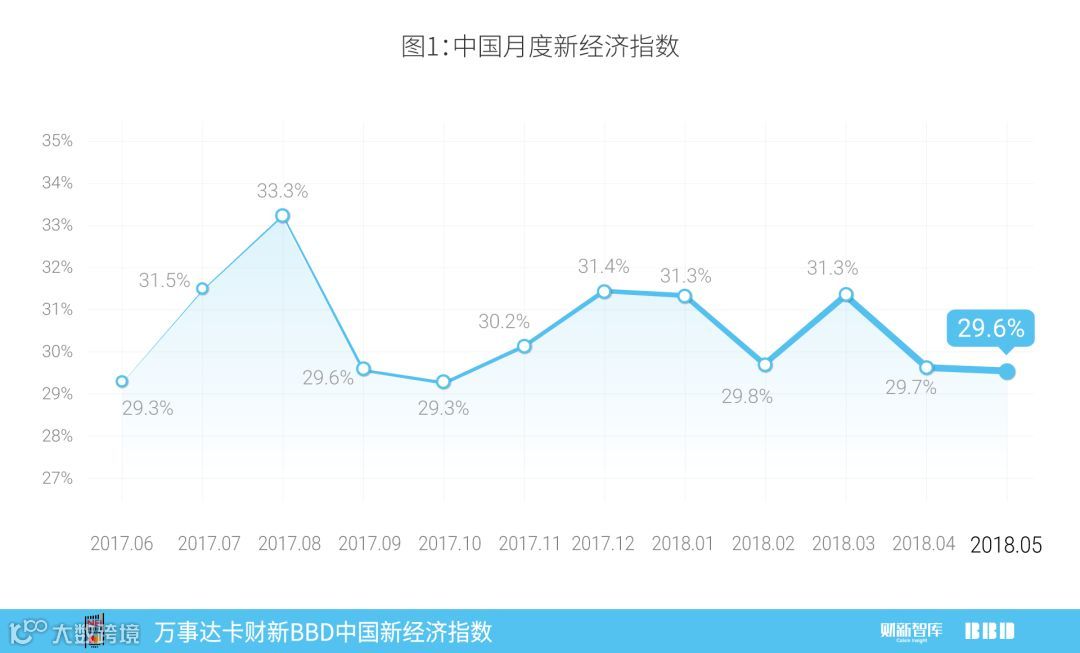
财新智库和BBD6月2日联合发布的数据显示,5月NEI录得29.6,即新经济投入占整个经济投入的比重为29.6%,较4月微降0.1个百分点。
NEI包括劳动力、资本和科技三项一级指标,在NEI中的权重分别是40%、35%和25%。
从分项指标来看,科技投入和资本投入下降是5月NEI下滑的主因。自去年10月以来,科技投入指数呈现震荡走势,5月录得 30.3,低于4月0.3个百分点;资本投入指数延续自2018年3月以来缓慢下降趋势,录得31.0,下降0.3个百分点;劳动力投入指数则与上月持平,录得 27.9。
从行业贡献度来看,新一代信息技术与信息服务产业居首位,5月贡献了11.4个百分点;新材料产业上升最快,贡献3.6个百分点,位列第二;高端装备制造业贡献率排名下降最剧烈,从上月的第二名降至第九名,仅贡献1.2个百分点。
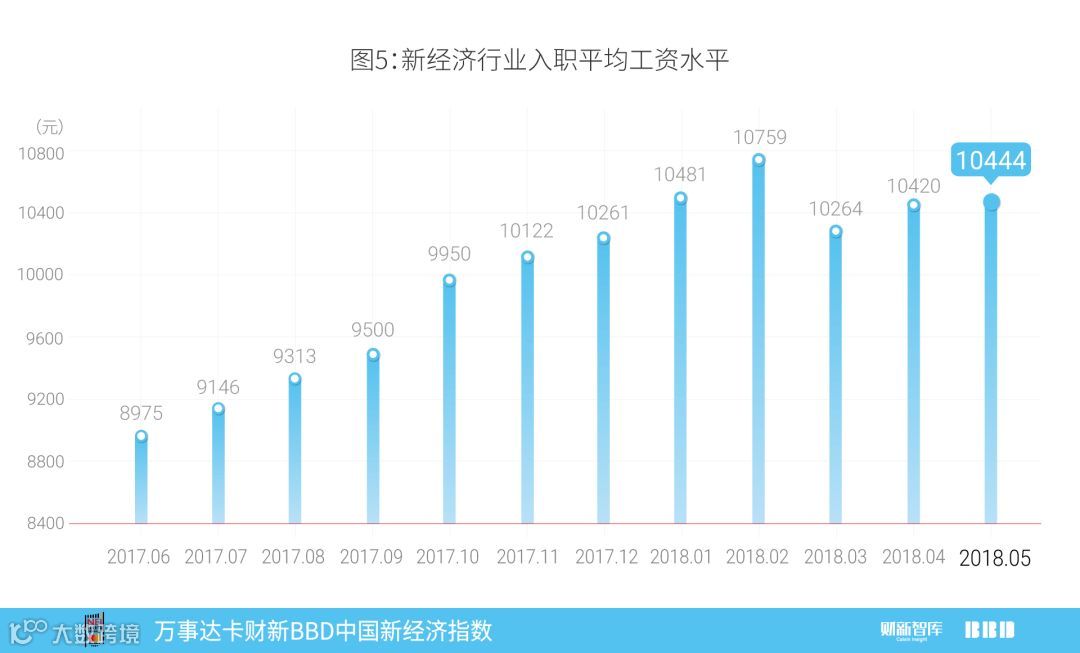
5月新经济行业入职平均月工资为10444元,较4月增加24元。但新经济行业招聘人数占全国总招聘人数比例有所下降,新经济行业招聘总薪酬占全国总薪酬比重则保持不变,这意味着新经济行业的平均入职工资水平相对于全国平均入职工资水平略有上升。总体来看,近期新经济行业的平均工资溢价仍低于2017年上半年。
从新增企业占总新增企业比重来看,近两年来建筑工程、建筑持续上升;传播、物流、电子商务持续下降;建材、信息、农业、教育、网络科技、房地产则波动较大。
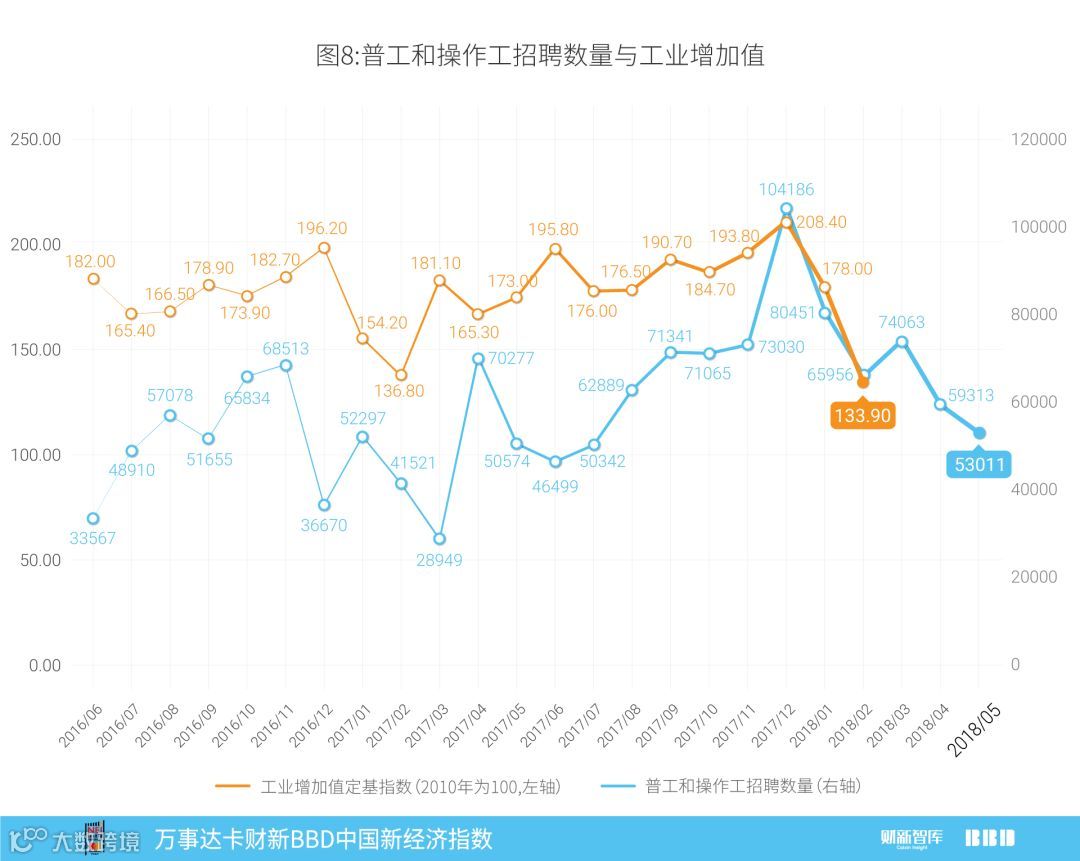
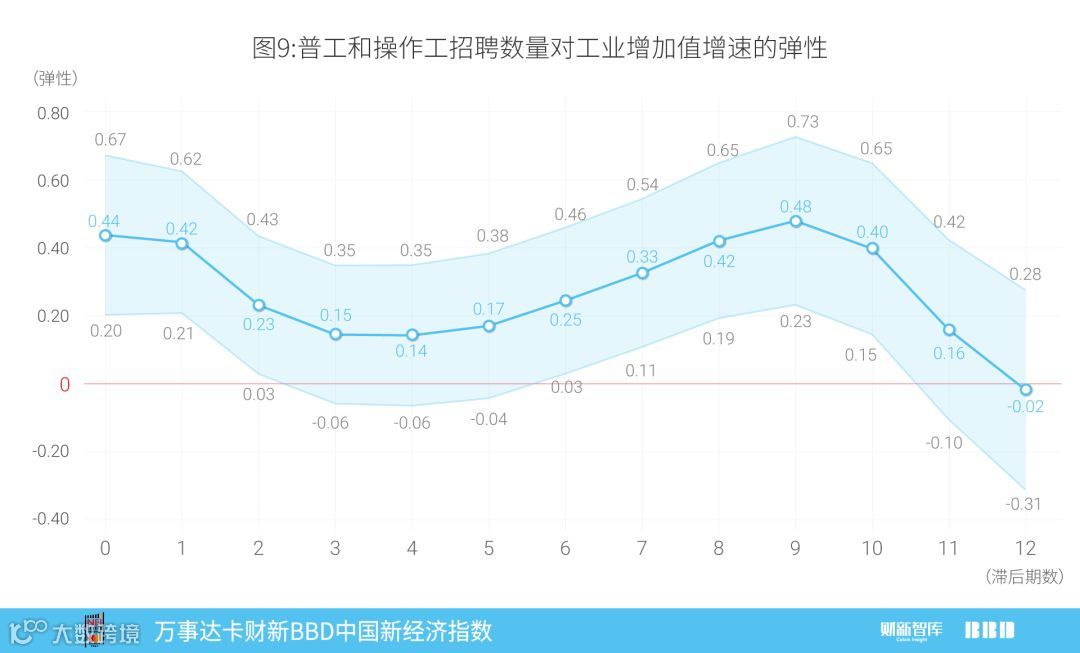
报告统计了低技能劳动力中普工和操作工的岗位需求数量,发现二者每月招聘总数与工业增加值定基指数(2010年为100)走势有很强的一致性。即使分地区来看,普工和操作工的招聘数量增速,仍对该地区工业增加值增速有很好的预测作用,其弹性系数约为0.4,即当普工和操作工的招聘数量增速上升1%时,该地区工业增加值增速会上升约0.4%。目前普工和操作工的需求量仍处于下滑通道,预计中国工业增加值增速会进一步降低。
按地区来看,2017年11月至2018年5月,广州、北京、杭州、上海、深圳在城市NEI排名中排行前五。
万事达卡财新BBD中国新经济指数,是由财新智库、成都数联铭品科技公司与北京大学国家发展研究院合作研发,每月2日上午10:00发布上月数据。
新经济指数旨在度量中国经济转型中新经济相对于传统经济或旧经济的活跃程度。新经济指数覆盖了节能与环保业、新一代信息技术与信息服务产业、生物医药产业、高端装备制造产业、新能源产业、新材料产业、新能源汽车产业、高新技术服务与研发业、金融服务与法律服务、体育文化和娱乐等10个类别,超过140个行业。
2018年5月
万事达卡财新BBD中国新经济指数

一、指数概览
2018年5月,万事达卡财新BBD中国新经济指数(NEI)录得29.6,即新经济投入占整个经济投入的比重为29.6%。2017年以来,NEI指数波动较大,按可比口径计算,本月NEI比上月微降0.1个百分点(图1)。本月NEI的下降主要来自科技投入和资本投入的下降。
NEI新经济据于以下定义:首先,高人力资本投入、高科技投入、轻资产;其次,可持续的较快增长;第三,符合产业发展方向。NEI所含行业详见《万事达卡财新BBD中国新经济指数技术报告》与《万事达卡财新BBD中国新经济指数报告(2017年3月)》。
二、主要分项指标
NEI包括劳动力、资本和科技三项一级指标,它们在NEI中的权重分别是40%、35%和25%。2018年5月NEI的下降主要来自科技投入和资本投入的下降。科技投入指数从2017年10月开始呈现震荡走势,本月指数录得30.3,环比下降0.3。资本投入指数从2018年3月以来缓慢下降,本月指数录得31.0,环比下降0.3。劳动力投入指数自2017年7月以来持续缓慢下降,本月环比持平,指数录得27.9(图2)。

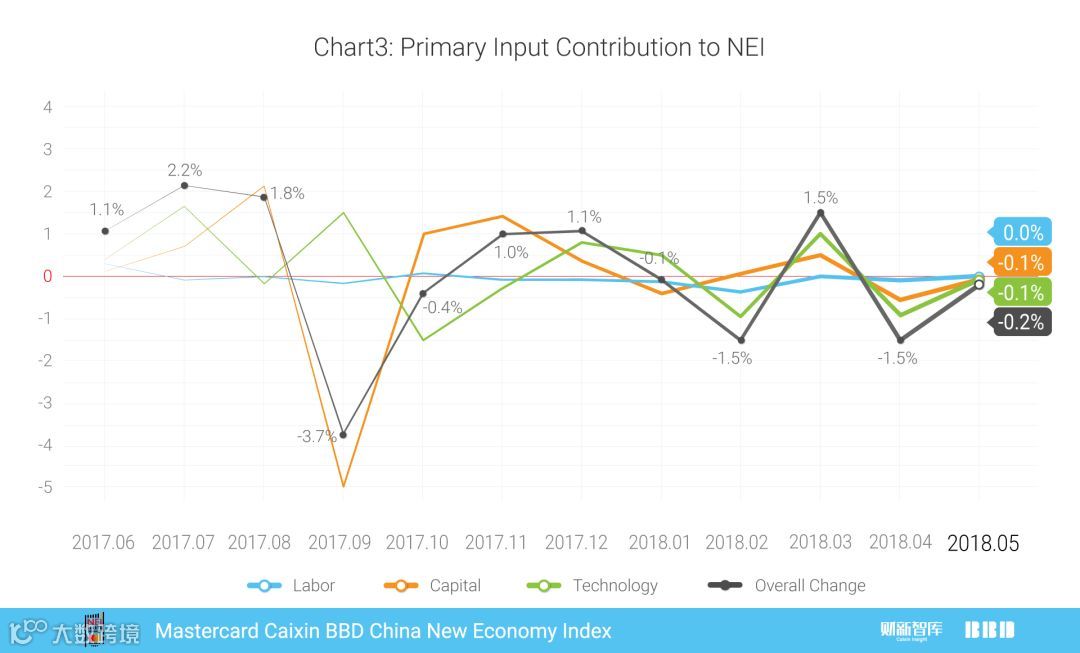
劳动力、资本和科技投入的变化绝对值分别为0.0,-0.1,和-0.1个百分点,与权重相乘求和后,对2018年5月NEI变化的贡献值为-0.2(图3)。

分行业看,NEI中占比最大的行业为新一代信息技术与信息服务产业,2018年5月为总指数贡献了11.4个百分点;本月名次上升最快的行业为新材料产业,贡献率为3.6个百分点,位列第二名;高端装备制造业贡献率排名下降最多,从上月的第二名下降至本月第九名,贡献率为1.2个百分点(图4)。

三、新经济就业
2018年5月,新经济行业入职平均工资水平环比上升,为每月10444元,较上月上升24元(图5)。新经济工资主要来自51job、智联招聘、拉钩、赶集网等数个招聘网站的招聘信息,即对劳动力的需求工资。
2018年5月新经济行业招聘总薪酬占全国总薪酬比重保持不变,仍为28.4%,同时新经济行业招聘人数占全国总招聘人数比例略有下降,为27.3%,这意味着新经济行业的平均入职工资水平相对于全国平均入职工资水平略有上升。2018年5月新经济入职工资“溢价”为4.0%,略高于上月3.9%(图6)。近几月新经济行业的平均工资溢价总体低于2017年上半年新经济行业的平均工资溢价。

四、从新增企业数据看投资行业变化
使用新增企业数据,我们可以对近两年来各行业新增企业占总新增企业比重进行监测,见图7。

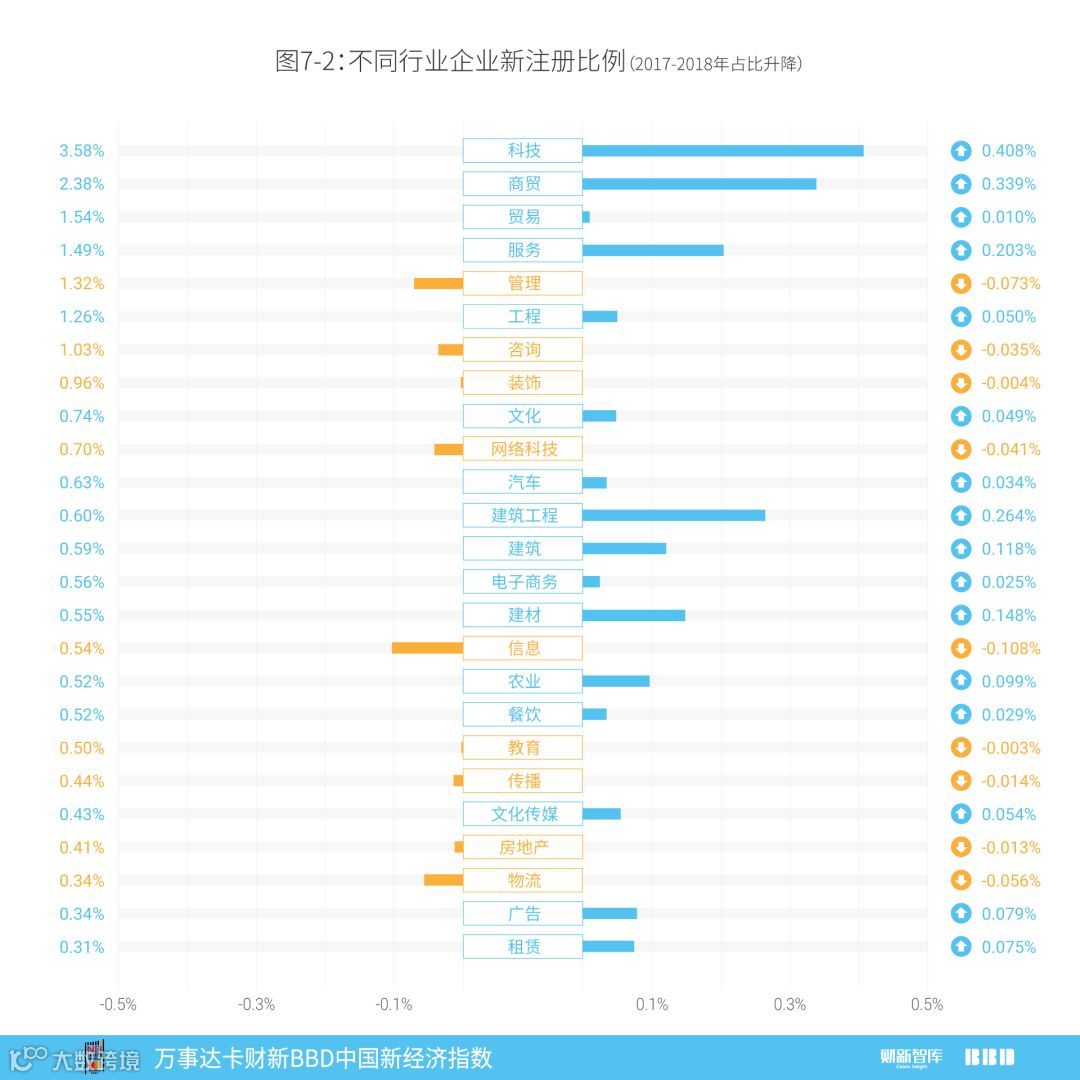
排名近两年连续上升的行业包括以下几类:建筑工程,2016年位列第25名,2017年上升到第23名,2018年继续上升到第12名,2017和2018年占比分别上升0.06%和0.26%;建筑,2016年位列第17名,2017年上升到第16名,2018年上升到第13名,2017和2018年占比分别上升0.05%和0.12%。
排名近两年持续下降的行业包括以下几类:传播,2016年位列第13名,2017年下降到第17名,2018年继续下降到第20名,2017和2018年占比分别下降0.13%和0.01%;物流,2016年位列第19名,2017年下降到第21名,2018年继续下降到第23名,2017和2018年占比分别下降0.00%和0.06%;电子商务,2016年位列第9名,2017年下降到第13名,2018年继续下降到第14名,2017和2018年占比分别变动0.29%和-0.02%。
排名在近两年之间波动变化的行业包括以下几类:建材,2016年位列第18名,2017年下降到第20名,2018年上升到第15名;信息,2016年位列第16名,2017年上升到第11名,2018年下降到第16名;农业,2016年位列第14名,2017年下降到第19名,2018年上升到第17名;教育,2016年位列第20名,2017年上升到第14名,2018年下降到第19名;网络科技,2016年位列第11名,2017年上升到第9名,2018年下降到第10名;房地产,2016年位列第23名,2017年上升到第18名,2018年下降到第22名。
五、从劳动力需求数据看工业增加值增速
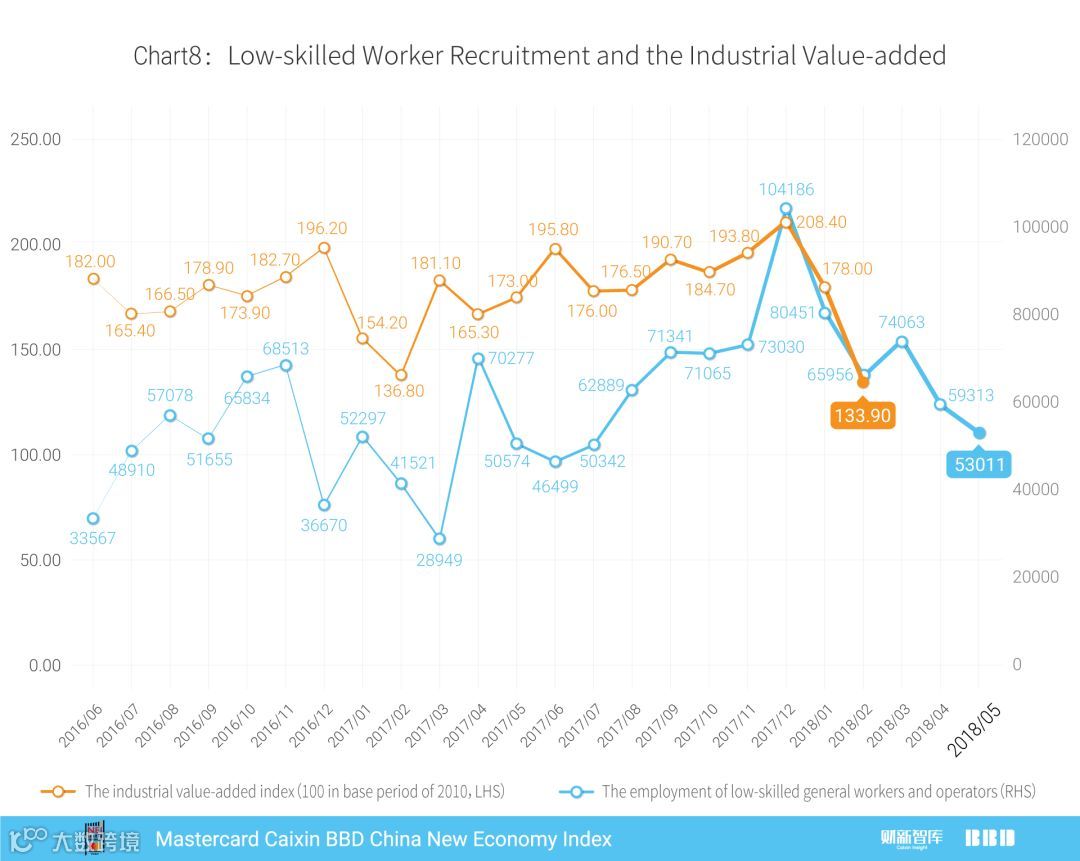
本期我们使用低技能劳动力中的普工和操作工这两项指标的数量,尝试对中国的工业增加值进行预测。首先,我们从各大招聘网站抓取普工和操作工的岗位需求情况,并将他们按月度汇总。从图8可以看到,普工和操作工的每月招聘总数,和工业增加值定基指数(2010年为100)的走势有很强的一致性,而普工和操作工的需求量仍然在下滑。因此,我们有理由认为,中国工业增加值的增速会进一步降低。
为了进一步验证该指标对于工业增加值预测的有效性,我们将普工和操作工的招聘分地区计算,并用每个地区普工/操作工招聘数量增速,来预测该地区的工业增加值增速。为了去除固定效应,我们在两个指标上均减去了该地区的3年平均值。结果见图9。我们发现,即使分地区之后,普工和操作工的招聘数量增速对该地区的工业增加值增速仍然有着很好的预测作用,其弹性系数约为0.4。该值的含义是,当普工和操作工的增速上升1%时,该地区的工业增加值增速会上升约0.4%。且该系数在滞后0期和滞后9期时最为显著。
六、城市新经济排名
2018年5月新经济总量城市排名前20名如图10所示,北京、上海、广州、杭州、深圳排名前五。该排序计算每个投入指标在所有城市中的排序百分位,再将百分位加权平均,体现的是近半年城市间新经济总量排名。

图11计算了2017年11月到2018年5月城市NEI平均排名,前五名为广州、北京、杭州、上海、深圳。

更多咨询敬请联络:
万事达卡
大中华区公共关系副总裁 吴焕宇
电话:+86-10-8519-9304
电邮:Huanyu_wu@mastercard.com
财新智库
财新智库高级经济学家 王喆
电话:+86-10-85905019
电邮:zhewang@caixin.com
公关总监 马玲
电话:+86-10-8590-5204
电邮:lingma@caixin.com
BBD(数联铭品)
BBD(数联铭品)首席经济学家 陈沁
电话:+86-28-65290823
电邮:chenqin@bbdservice.com
版权声明
万事达卡财新BBD中国新经济指数,是由财新智库(深圳)投资发展有限公司和成都数联铭品科技公司共同研发,与北京大学国家发展研究院合作,经过近一年努力,于2016年3月2日在北京首发的指数产品,此后每月2日上午10:00发布上月数据。
关于万事达卡:
万事达卡(纽交所股票交易代码:MA),www.mastercard.cn,是全球性的支付与科技公司。通过运营全球最快的支付处理网络,万事达卡将超过210个国家和地区的消费者、金融机构、商户、政府和企业连接在一起。万事达卡的产品和解决方案使得每个人在购物、旅行、企业经营、财务管理等日常商业活动都变得更容易、更安全和更高效。敬请关注我们的“万事达卡”官方微信以及在新浪的官方微博@万事达人,以获悉动态并参与互动。也可访问万事达卡新闻中心或万事达卡互动中心获取更多资讯。
关于财新:
财新传媒是提供财经新闻的全媒体集团,依托专业的团队和强大的原创新闻优势,以网站、移动端、期刊、视频、图书、会议等 多层次的业务平台,为中国最具影响力的受众群,提供准确、全面、深入的财经新闻产品。财新智库是财新传媒通过孵化另行建立的高端金融资讯服务平台,旨在通过发展金融数据业务,壮大宏观经济研究队伍,服务于智库业务客户。详细信息,敬请浏览 www.caixin.com。
关于BBD:
BBD(数联铭品)是行业领先的大数据解决方案提供商,紧密围绕新经济,通过动态尽调、信用评级、风险定价和经济指数四个步骤,BBD提供从微观到宏观的大数据服务。详细信息,敬请浏览:http://www.bbdservice.com。
May 2018
Mastercard Caixin BBD China New Economy Index

Overview
In May 2018, the Mastercard Caixin BBD New Economy Index (NEI) reading came in at 29.6, indicating that the New Economy accounted for 29.6% of overall economic input activities that month, down 0.1 ppts from April (Chart 1). The declining NEI was due to the decrease of technology input and capital input. New economy is defined as following: 1) human capital intensive, technology intensive and capital light; 2) sustainable rapid growth, and 3) in line with the strategic new industries defined by the government. Please refer to our previous reports (March 2016 and March 2017) for the list of NEI sectors.

Primary Inputs
The NEI includes labor, capital and technology inputs that account for 40%, 35% and 25% of the total weights of the index, respectively. The decline in the May NEI reading came from the decrease of technology input and capital input (Chart 2). Technology input index fluctuated widely since October 2017, coming in at 30.3, with 0.3 MoM decrease. Capital investment showed a slow downtrend since March 2018, it continued to decline to 31.0 this month, with 0.3 MoM decrease. Labor input index declined moderately since July 2017, remaining to 27.9 this month.

Taking the weight into account, percentage changes in labor, capital and technology inputs were 0.0, -0.1, and -0.1 ppts, respectively. The net NEI change was -0.2 ppts in total (Chart 3).
Looking at the sectors, the New IT industry formed the largest proportion of the New Economy Index, contributing 11.4 ppts to NEI. Advanced Materials was the industry with fastest growth in May, contributing 3.6 ppts and ranking the second. Advanced Equipment Manufacturing came ninth from second, the biggest drop in ranking, contributing 1.2 ppts in May (Chart 4).

New Economy Employment
In May 2018, the average monthly entry level salary of the New Economy was RMB 10,444 per month, increasing from last month’s level of RMB 10,420 (Chart 5). New Economy wage information is compiled from online websites of career platforms and recruitment services including 51job and Zhaopin, as well as other sites that list job demands.

Hiring in the New Economy sectors accounted for 27.3% of total hiring in May, slightly lower than the previous month’s 27.4%. At the same time, the total compensation share of New Economy sectors remained stable to 28.4%, which meant the average entry salary level of New Economy was higher than national average entry wage level. The entry level salary premium of the New Economy was 4.0% as compared to economy-wide counterparts, increasing from 3.9% in April (Chart 6). In the recent half year, the average salary premium of the New Economy was lower than the first half year generally.

Decomposition of New Established Enterprises
We use newly-established enterprises data to monitor new enterprises in sub-sectors (Chart 7).


Sub-sectors which were continuously ranking up in last 2 years include the following: Architectural Engineering (No.25 in 2016, rising to No.23 and No.12 in 2017 and 2018, 0.06% and 0.26% increase in proportion in 2017 and 2018 respectively); Construction (No. 17 in 2016, rising to No. 16 and No. 13 in 2017 and 2018, 0.05% and 0.12% increase in proportion 2017 and 2018 respectively).
Sub-sectors which were continuously ranking down in 2 last years include the following: Communication (No. 13 in 2016, dropping to No. 17 and No. 20 in 2017 and 2018, 0.13% and 0.01% decrease in proportion 2017 and 2018 respectively); Logistics (No. 19 in 2016, dropping to No. 21 and No. 23 in 2017 and 2018, 0.00% and 0.06% decrease in proportion 2017 and 2018 respectively); E-commerce (No. 9 in 2016, dropping to No. 13 and No. 14 in 2017 and 2018, 0.29% increase and 0.02% decrease in proportion 2017 and 2018 respectively)
Sub-sectors with fluctuating ranks in last 2 years include the following: Materials (No.18 in 2016, dropped to No.20 in 2017 and rose to No 15 in 2018); Information (No.16 in 2016, rose to No.11 in 2017 and dropped to No 16 in 2018); Agriculture (No.14 in 2016, dropped to No.19 in 2017 and rose to No 17 in 2018); Education (No.20 in 2016, rose to No.14 in 2017 and dropped to No 19 in 2018); IT (No.11 in 2016, rose to No.9 in 2017 and dropped to No 10 in 2018); Real Estate (No.23 in 2016, rose to No.18 in 2017 and dropped to No 22 in 2018).
Industrial Value-Added Based and Employment Data
This month, we explored China’s industrial value-added by the employment of low-skilled general workers and operators. Monthly data in general workers and operators recruitment were collected from online websites of career platforms. It can be seen that the total employment of general workers and operators is reasonably consistent with the industrial value-added index (100 in base period of 2010) (Chart 8).
We analyzed the employment data of general workers and operators in different provincial areas as well. The growth rates of low-skilled workers and industrial value-added in each region were compared. To remove the fixed effect, we de-trended the series by subtracting the three-year average. Similar consistency was found between growth rate of employment and that of industrial value-added across regions (Chart 9). The elasticity is around 0.4, indicating when the hiring growth rates of general workers and the operators increase by 1%, the growth rate of industry value added will increase by about 0.4%. The coefficient was the most significant with the 9-month lag or no lag at all.

City Rankings of the New Economy
Based on overall New Economy rankings, the top twenty cities were shown in Chart 10. The top five cities were Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Hangzhou and Shenzhen. Rankings are based on a weighted average of the percentile rank of indicators for the city in the past 6 months.

Chart 11 showed the average NEI city rankings between November 2017 and May 2018. The top five cities were Guangzhou, Beijing, Hangzhou, Shanghai and Shenzhen.

For further information please contact:
Mastercard
Mr. Wu Huanyu, Director, Communications
Tel:+86-10-8519-9304
Email:Huanyu_wu@mastercard.com
Caixin Insight Group
Dr. Wang Zhe, Senior Economist
Tel:+86-10-85905019
Emails:zhewang@caixin.com
Ma Ling, Public Relations
Tel:+86-10-8590-5204
Email:lingma@caixin.com
BBD
Dr. Chen Qin, Chief Economist
Tel:+86-28-65290823
Emails:chenqin@bbdservice.com
The Mastercard Caixin BBD China New Economy Index is the fruit of a research partnership between Caixin Insight Group and BBD, in collaboration with the National Development School, Peking University. The subject of a year of research, the NEI was first publically released on March 2, 2016 and will be issued the 2nd of every month at 10:00am China Standard Time.
About Caixin
Caixin Media is China's leading media group dedicated to providing financial and business news through periodicals, online content, mobile applications, conferences, books and TV/video programs. Caixin Media aims to blaze a trail that helps traditional media prosper in the new media age through integrated multimedia platforms. Caixin Insight Group is a high-end financial data and analysis platform. For more information, please visitwww.caixin.com.
About Mastercard
Mastercard (NYSE: MA), www.mastercard.com, is a technology company in the global payments industry. We operate the world’s fastest payments processing network, connecting consumers, financial institutions, merchants, governments and businesses in more than 210 countries and territories. Mastercard’s products and solutions make everyday commerce activities – such as shopping, traveling, running a business and managing finances – easier, more secure and more efficient for everyone. Follow us on Twitter @MastercardAP and @MastercardNews, join the discussion on the Beyond the Transaction Blog and subscribe for the latest news on the Engagement Bureau.
About BBD (Business Big Data)
BBD is a leading Big Data and quantitative business analytics firm specializing in the analysis of the high-growth industries emerging in Mainland China. Through dynamic data tracking, credit analysis, risk pricing and economic index construction, BBD provides its clients with a wide range of services at both the macro and micro level. For more information, please visit http://www.bbdservice.com/.



