计算电磁学包含了广泛的应用领域,包括天线、纳米光子学、太阳能电池、超材料、激光等等。在这些不同的领域中,也有许多方法来进行所需的计算。电磁模拟有三种主要的数值方法:FDTD, FEM和MOM。每种方法都最适合特定的情况,各有优缺点。在这篇文章中,汇总这些方法的一些最好的开源实现的参考资料(附链接)。
FDTD:
Meep. https://meep.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
gprMax. https://www.gprmax.com/
OpenEMS. http://openems.de/index.php/Tutorials
FEM:
FEniCS. https://fenicsproject.org/
Elmer FEM. http://www.elmerfem.org/blog/
FreeFEM. https://freefem.org/
MOM:
Bempp. http://bempp.com/
PumaEM. https://github.com/Gjacquenot/Puma-EM
NEC-2. https://github.com/tmolteno/necpp


As shown below👇
三大算法简介
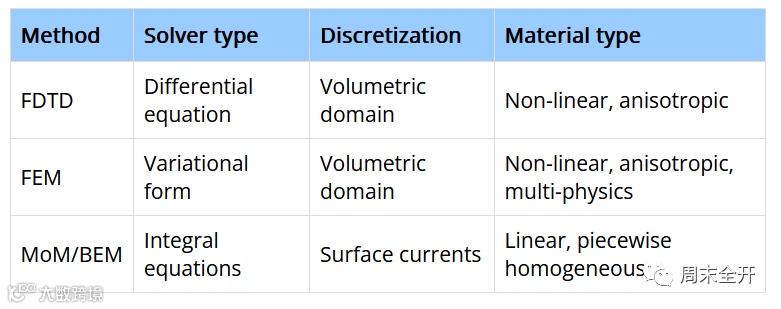
FDTD算法:采用差分直接离散时域Maxwell方程,电磁场的求解基于时间步的迭代,无需存储全空间的电磁场信息,内存消耗较小,同时采用立方体网格和差分算法,网格形式和算法均十分简单,计算速度也贼快,基于时域算法,特别适合“宽带问题”的求解。但是,简单的立方体方体网格带来的弊端就是模型拟合精度较低,对于含有精细结构的模型,计算精度较低,同时基于“微分方程”,计算区域需要设置截断。FDTD比较适合于不含有较多精细结构的电大尺寸模型的电性能计算以及宽带问题的计算;
FEM算法:采用四面体网格对目标进行离散,拟合精度比FDTD算法更高,计算精度也要明显优于FDTD算法。但是,FEM基于频域/微分算法,需要同时对整个区域内的电磁场信息进行求解和存储,内存消耗大,计算速度慢,计算模型的电尺寸也相对较小。FEM主要适合于微波电路器件,天线等目标“辐射问题”的精确计算;
MoM算法:通过“场-源关系”,将“场”的求解问题转化为“源”求解问题,采用的基函数“格林函数”天然满足辐射条件,无需设置截断,计算精度高,同时矩阵的计算采用直接计算,不存在收敛性的问题,同时由于网格的剖分仅存在于目标体表面或内部,未知量数目大幅降低,矩阵规模小于FDTD和FEM,但是由于“源”之间均存在耦合,因此矩阵为“稠密”矩阵,计算复杂度大,计算速度慢。MoM主要适合于含有精细结构的电小尺寸目标“散射问题”的精确计算;
三大算法的开源代码
1、三大算法的区别
2、fdtd最流行的开源代码

Meep.
https://meep.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
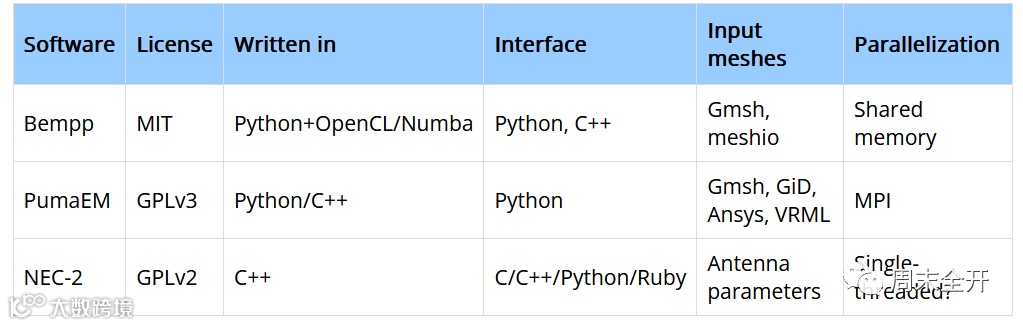
Developed at MIT, Meep is a highly efficient FDTD package, scriptable in Python, Scheme or callable from C++ APIs. It is parallelized with MPI, and it includes a library with support for a variety of material types.
gprMax.
https://www.gprmax.com/
Developed at the University of Edinburgh, gprMax was designed for modelling Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) but can also be used to model electromagnetic wave propagation for many other applications. gprMax is command-line driven software written in Python, with performance-critical parts written in Cython/OpenMP.
OpenEMS.
http://openems.de/index.php/Tutorials
Developed at the University of Duisburg-Essen, and parallelized with MPI. Matlab or Octave are used as a scripting interfaces.
3、FEM最好的开源代码

FEniCS.
https://fenicsproject.org/
FEniCS is a popular open-source LGPLv3-licenced software package for solving partial differential equations (PDEs). It features high-level Python and C++ interfaces, and can be run in high-performance clusters. To get started, visit the FEniCS Tutorial which includes an example in magnetostatics, or check out the official Discourse forum.
Elmer FEM.
http://www.elmerfem.org/blog/
An open-source Finite Element Solver, dealing with multiphysical simulations. Built-in Electromagnetics Solvers include magnetostatic, electrostatic and wave-equation solvers. See the Elmer Models Manual for more information. Elmer has a GUI, a command-line interface, and a Python wrapper pyelmer.
FreeFEM.
https://freefem.org/
FreeFEM is an open-source LGPLv3-licenced PDE solver relying on its own programming language. FreeFEM offers a large list of finite elements. Pre-built physics for Electromagnetic simulations include Magnetostatics and Electrostatics only.
4、MOM最流行的开源代码
Bempp.
http://bempp.com/
Bempp is an open-source, MIT licenced, computational boundary element platform to solve electrostatic, acoustic and electromagnetic problems. Bempp uses just-in-time compiled OpenCL or Numba kernels to assemble BEM operators in CPUs or GPUs. Features include a Python interface, Fast Multipole Method acceleration via Exafmm-t, and coupled FEM/BEM computations via interfaces to FEniCS.
PumaEM
https://github.com/Gjacquenot/Puma-EM
PumaEM is an open-source (GPL v3 licensed) Method of Moments implementation for Electromagnetics, accelerated with the Multilevel Fast Multipole Method, and parallelized via MPI.
NEC-2.
https://github.com/tmolteno/necpp
A classical code by LLNL rewritten in C++, targeted at wire and surface antenna simulation.
参考:
https://www.matecdev.com/posts/differences-fdtd-fem-mom.html#the-method-of-moments-mom-or-bem-in-electromagnetics
缘起“收敛性”——Maxwell方程与求解
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg3NjM4MDcwMQ==&mid=2247483923&idx=1&sn=1e3012e5d4a05ba01888e0feeb55e7a7&chksm=cf325561f845dc7733c3e540b95060aee97fd43727bfd14a14f773c16b052a1c558163bdf25b&scene=21#wechat_redirect




