微信公众号:九极客
欢迎星标关注九极客,一起探讨技术与架构!
大家的点赞、收藏和评论很重要,如文章对您有帮助还请转发支持下,谢谢!

亿级流量下的系统架构演进与实战指南
在数字化时代,高并发已成为各类互联网应用的标配能力。根据2024年最新行业数据,头部电商平台的峰值QPS已突破100万次,而短视频平台的并发用户数更是达到亿级规模。面对如此巨大的流量冲击,如何设计稳定可靠的高并发系统,成为每个架构师必须掌握的硬核技能。

负载均衡:流量分发的艺术
负载均衡的核心原理与算法
负载均衡作为高并发系统的第一道防线,其作用是将海量请求合理分配到多个服务节点,避免单点过载。
负载均衡算法深度解析
不同的业务场景需要选择合适的负载均衡算法,以达到最优的资源利用和性能表现。
/**
* 负载均衡算法实现集
*/
public class LoadBalancerAlgorithms {
/**
* 轮询算法 - 均匀分配请求
*/
public class RoundRobinLoadBalancer {
private final List<Server> servers;
private final AtomicInteger currentIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
public Server selectServer() {
int index = currentIndex.getAndUpdate(i -> (i + 1) % servers.size());
return servers.get(index);
}
}
/**
* 加权轮询算法 - 考虑服务器处理能力
*/
public class WeightedRoundRobinLoadBalancer {
private final List<WeightedServer> servers;
private final AtomicInteger currentWeight = new AtomicInteger(0);
private final int maxWeight;
private final int gcdWeight;
public Server selectServer() {
while (true) {
int current = currentWeight.getAndUpdate(i -> (i + 1) % maxWeight);
for (WeightedServer server : servers) {
if (current % server.getWeight() == 0) {
return server;
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 最少连接算法 - 动态感知服务器负载
*/
public class LeastConnectionsLoadBalancer {
private final Map<Server, AtomicInteger> connectionCounts;
public Server selectServer() {
return connectionCounts.entrySet().stream()
.min(Map.Entry.comparingByValue(Comparator.comparing(AtomicInteger::get)))
.map(Map.Entry::getKey)
.orElseThrow(() -> new NoAvailableServerException());
}
public void releaseConnection(Server server) {
connectionCounts.get(server).decrementAndGet();
}
}
/**
* 一致性哈希算法 - 减少缓存失效
*/
public class ConsistentHashLoadBalancer {
private final SortedMap<Integer, Server> circle = new TreeMap<>();
private final int virtualNodes;
public Server selectServer(String key) {
if (circle.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
int hash = hashFunction(key);
SortedMap<Integer, Server> tailMap = circle.tailMap(hash);
int nodeHash = tailMap.isEmpty() ? circle.firstKey() : tailMap.firstKey();
return circle.get(nodeHash);
}
private int hashFunction(String key) {
// 使用MurmurHash等高质量的哈希函数
return Hashing.murmur3_32().hashString(key, StandardCharsets.UTF_8).asInt();
}
}
}四层与七层负载均衡的抉择
在实际架构设计中,我们需要根据业务特性选择合适的负载均衡层级。
四层负载均衡(L4)
/**
* 四层负载均衡配置示例
* 基于IP和端口的流量分发
*/
public class Layer4LoadBalancing {
@Configuration
public class L4LoadBalancerConfig {
@Bean
public LoadBalancer tcpLoadBalancer() {
return LoadBalancerBuilder
.newBuilder()
.build();
}
// Nginx四层负载均衡配置示例
// stream {
// upstream backend_servers {
// server 192.168.1.10:8080;
// server 192.168.1.11:8080;
// server 192.168.1.12:8080;
// }
//
// server {
// listen 80;
// proxy_pass backend_servers;
// }
// }
}
}七层负载均衡(L7)
/**
* 七层负载均衡实现
* 基于HTTP协议的内容感知路由
*/
public class Layer7LoadBalancing {
@Configuration
public class L7LoadBalancerConfig {
@Bean
public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> loadBalancerRouter() {
return RouterFunctions.route()
.GET("/api/users/{id}",
request -> {
String userId = request.pathVariable("id");
Server targetServer = userServiceLoadBalancer.selectServer(userId);
return ServerResponse.temporaryRedirect(
URI.create(targetServer.getUrl() + "/api/users/" + userId))
.build();
})
.POST("/api/orders",
request -> {
Server targetServer = orderServiceLoadBalancer.selectServer();
return ServerResponse.temporaryRedirect(
URI.create(targetServer.getUrl() + "/api/orders"))
.build();
})
.build();
}
// Nginx七层负载均衡配置示例
// http {
// upstream backend {
// server 192.168.1.10:8080 weight=3;
// server 192.168.1.11:8080 weight=2;
// server 192.168.1.12:8080 weight=1;
//
// # 健康检查
// check interval=3000 rise=2 fall=3 timeout=1000;
// }
//
// server {
// listen 80;
//
// location /api/ {
// proxy_pass http://backend;
// proxy_set_header Host $host;
// proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
// }
// }
// }
}
}
缓存架构:性能加速的关键
多级缓存体系设计
构建高效的多级缓存体系是提升系统性能的重要手段。
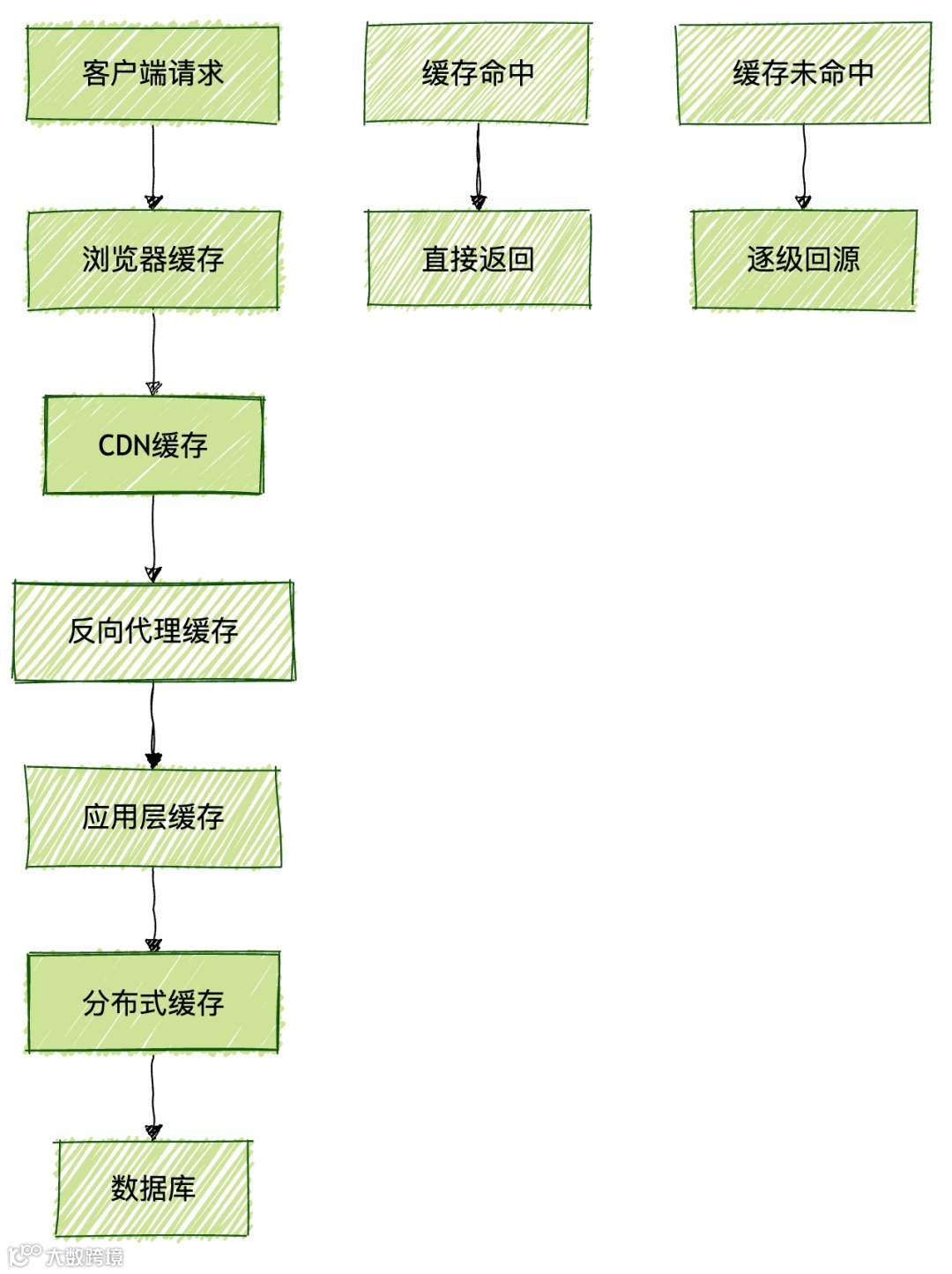
应用级缓存实现
/**
* 多级缓存实现框架
*/
public class MultiLevelCacheSystem {
/**
* 缓存层级管理器
*/
@Service
public class CacheManager {
private final LocalCache localCache;
private final DistributedCache distributedCache;
private final CacheLoader cacheLoader;
@Value("${cache.local.ttl:300}")
private long localTtl;
@Value("${cache.redis.ttl:3600}")
private long redisTtl;
/**
* 多级缓存读取
*/
public <T> T get(String key, Class<T> clazz) {
// 第一级:本地缓存
T value = localCache.get(key, clazz);
if (value != null) {
metrics.recordLocalCacheHit();
return value;
}
// 第二级:分布式缓存
value = distributedCache.get(key, clazz);
if (value != null) {
// 回填本地缓存
localCache.set(key, value, localTtl);
metrics.recordDistributedCacheHit();
return value;
}
// 第三级:数据源加载
value = cacheLoader.load(key, clazz);
if (value != null) {
// 异步回填缓存
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
distributedCache.set(key, value, redisTtl);
localCache.set(key, value, localTtl);
});
metrics.recordCacheMiss();
}
return value;
}
}
/**
* 本地缓存实现 - Caffeine
*/
@Configuration
public class LocalCacheConfig {
@Bean
public Cache<String, Object> localCache() {
return Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(10_000)
.expireAfterWrite(5, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.recordStats()
.build();
}
}
/**
* 分布式缓存实现 - Redis
*/
@Configuration
public class RedisCacheConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate() {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory());
template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
return template;
}
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager cacheManager() {
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofHours(1))
.disableCachingNullValues();
return RedisCacheManager.builder(redisConnectionFactory())
.cacheDefaults(config)
.build();
}
}
}缓存策略与一致性保障
缓存更新策略
/**
* 缓存更新策略实现
*/
public class CacheUpdateStrategies {
/**
* 写穿透策略
*/
@Service
@Transactional
public class WriteThroughStrategy {
public <T> void updateWithWriteThrough(String key, T value) {
// 先更新数据库
database.update(value);
// 再更新缓存
cache.set(key, value);
}
}
/**
* 写回策略
*/
@Service
public class WriteBackStrategy {
private final WriteBuffer writeBuffer;
@Async
public <T> void updateWithWriteBack(String key, T value) {
// 先更新缓存
cache.set(key, value);
// 异步批量更新数据库
writeBuffer.add(new WriteTask(key, value));
}
}
/**
* 缓存删除策略
*/
@Service
public class CacheAsideStrategy {
public <T> void updateWithCacheAside(String key, T value) {
// 先更新数据库
database.update(value);
// 再删除缓存
cache.delete(key);
}
public <T> T getWithCacheAside(String key, Class<T> clazz) {
T value = cache.get(key, clazz);
if (value == null) {
value = database.load(key, clazz);
if (value != null) {
cache.set(key, value);
}
}
return value;
}
}
}缓存一致性解决方案
/**
* 缓存一致性保障机制
*/
public class CacheConsistency {
/**
* 基于消息队列的最终一致性
*/
@Service
public class MessageQueueConsistency {
private final RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
private final KafkaTemplate<String, Object> kafkaTemplate;
@EventListener
public void handleDatabaseUpdate(DatabaseUpdateEvent event) {
// 发布数据库变更事件
kafkaTemplate.send("cache-invalidation",
new CacheInvalidationMessage(event.getKey(), event.getOperation()));
}
@KafkaListener(topics = "cache-invalidation")
public void processCacheInvalidation(CacheInvalidationMessage message) {
// 处理缓存失效
switch (message.getOperation()) {
case UPDATE:
case DELETE:
redisTemplate.delete(message.getKey());
break;
case CREATE:
// 可以选择不处理,等待下次读取时加载
break;
}
}
}
/**
* 分布式锁保障强一致性
*/
@Service
public class DistributedLockConsistency {
private final RedissonClient redissonClient;
public <T> T updateWithLock(String key, T newValue, Class<T> clazz) {
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock("cache_update_lock:" + key);
try {
lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 在锁内执行更新操作
database.update(newValue);
cache.delete(key);
return newValue;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
数据库分库分表:数据层面的水平扩展
分库分表的核心策略
当单表数据量达到千万级别时,分库分表成为必然选择。

分片策略选择
/**
* 分库分表策略实现
*/
public class ShardingStrategies {
/**
* 基于用户ID的取模分片
*/
public class UserIdShardingStrategy implements ShardingStrategy {
private final int databaseCount = 4;
private final int tableCount = 8;
@Override
public String determineDataSource(String userId) {
int dbIndex = Math.abs(userId.hashCode()) % databaseCount;
return "user_db_" + dbIndex;
}
@Override
public String determineTableName(String userId) {
int tableIndex = Math.abs(userId.hashCode()) % tableCount;
return "user_info_" + tableIndex;
}
}
/**
* 基于时间范围的分片
*/
public class TimeBasedShardingStrategy implements ShardingStrategy {
@Override
public String determineDataSource(LocalDateTime createTime) {
int year = createTime.getYear();
// 每年一个数据库
return "order_db_" + year;
}
@Override
public String determineTableName(LocalDateTime createTime) {
int month = createTime.getMonthValue();
// 每月一个表
return "order_info_" + month;
}
}
/**
* 一致性哈希分片
*/
public class ConsistentHashShardingStrategy implements ShardingStrategy {
private final ConsistentHash<DataSource> dataSourceHash;
private final ConsistentHash<Table> tableHash;
@Override
public String determineDataSource(String shardingKey) {
DataSource dataSource = dataSourceHash.get(shardingKey);
return dataSource.getName();
}
}
}ShardingSphere实战配置
分库分表配置示例
# ShardingSphere数据分片配置
spring:
shardingsphere:
datasource:
names: ds0, ds1, ds2, ds3
ds0:
type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/user_db_0
username: root
password: password
ds1:
# ... 类似配置
ds2:
# ... 类似配置
ds3:
# ... 类似配置
sharding:
tables:
user_info:
actual-data-nodes: ds${0..3}.user_info_${0..7}
database-strategy:
standard:
sharding-column: user_id
precise-algorithm-class-name: com.example.UserIdDatabaseShardingAlgorithm
table-strategy:
standard:
sharding-column: user_id
precise-algorithm-class-name: com.example.UserIdTableShardingAlgorithm
key-generator:
column: id
type: SNOWFLAKE
props:
sql:
show: true自定义分片算法实现
/**
* 自定义分片算法实现
*/
public class CustomShardingAlgorithms {
/**
* 用户ID数据库分片算法
*/
public class UserIdDatabaseShardingAlgorithm implements PreciseShardingAlgorithm<String> {
private final int databaseCount = 4;
@Override
public String doSharding(Collection<String> availableTargetNames,
PreciseShardingValue<String> shardingValue) {
String userId = shardingValue.getValue();
int databaseIndex = Math.abs(userId.hashCode()) % databaseCount;
return availableTargetNames.stream()
.filter(name -> name.endsWith(String.valueOf(databaseIndex)))
.findFirst()
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("未找到对应的数据库"));
}
}
/**
* 用户ID表分片算法
*/
public class UserIdTableShardingAlgorithm implements PreciseShardingAlgorithm<String> {
private final int tableCount = 8;
@Override
public String doSharding(Collection<String> availableTargetNames,
PreciseShardingValue<String> shardingValue) {
String userId = shardingValue.getValue();
int tableIndex = Math.abs(userId.hashCode()) % tableCount;
String logicTableName = shardingValue.getLogicTableName();
String actualTableName = logicTableName + "_" + tableIndex;
return availableTargetNames.stream()
.filter(name -> name.equals(actualTableName))
.findFirst()
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("未找到对应的数据表"));
}
}
}
读写分离与数据库优化
读写分离架构
通过读写分离将读操作和写操作分发到不同的数据库实例,提升系统整体吞吐量。
/**
* 读写分离配置与实现
*/
public class ReadWriteSeparation {
/**
* Spring Boot多数据源配置
*/
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class DataSourceConfig {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.master")
public DataSource masterDataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.slave")
public DataSource slaveDataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean
public DataSource routingDataSource() {
Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources = new HashMap<>();
targetDataSources.put("master", masterDataSource());
targetDataSources.put("slave", slaveDataSource());
ReadWriteSplitRoutingDataSource routingDataSource =
new ReadWriteSplitRoutingDataSource();
routingDataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(masterDataSource());
routingDataSource.setTargetDataSources(targetDataSources);
return routingDataSource;
}
}
/**
* 读写分离路由数据源
*/
public class ReadWriteSplitRoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly() ?
"slave" : "master";
}
}
/**
* 基于注解的读写分离
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ReadOnly {
}
@Aspect
@Component
public class ReadWriteSeparationAspect {
@Around("@annotation(readOnly)")
public Object proceed(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, ReadOnly readOnly) throws Throwable {
try {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionReadOnly(true);
return joinPoint.proceed();
} finally {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionReadOnly(false);
}
}
}
}数据库连接池优化
/**
* 数据库连接池优化配置
*/
public class ConnectionPoolOptimization {
@Configuration
public class HikariCPConfig {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.hikari")
public DataSource dataSource() {
HikariConfig config = new HikariConfig();
// 连接池大小配置
config.setMaximumPoolSize(20);
config.setMinimumIdle(10);
config.setConnectionTimeout(30000);
config.setIdleTimeout(600000);
config.setMaxLifetime(1800000);
// 优化配置
config.setConnectionTestQuery("SELECT 1");
config.setValidationTimeout(5000);
config.setLeakDetectionThreshold(60000);
// 针对高并发的优化
config.addDataSourceProperty("cachePrepStmts", "true");
config.addDataSourceProperty("prepStmtCacheSize", "250");
config.addDataSourceProperty("prepStmtCacheSqlLimit", "2048");
config.addDataSourceProperty("useServerPrepStmts", "true");
config.addDataSourceProperty("useLocalSessionState", "true");
config.addDataSourceProperty("rewriteBatchedStatements", "true");
config.addDataSourceProperty("cacheResultSetMetadata", "true");
config.addDataSourceProperty("cacheServerConfiguration", "true");
config.addDataSourceProperty("elideSetAutoCommits", "true");
config.addDataSourceProperty("maintainTimeStats", "false");
return new HikariDataSource(config);
}
}
}
消息队列:异步解耦与流量削峰
消息队列在高并发系统中的应用
/**
* 基于消息队列的异步处理架构
*/
public class MessageQueueArchitecture {
/**
* 订单创建异步处理示例
*/
@Service
public class OrderService {
private final KafkaTemplate<String, Object> kafkaTemplate;
private final OrderRepository orderRepository;
@Transactional
public void createOrder(Order order) {
// 同步操作:保存订单核心数据
orderRepository.save(order);
// 异步操作:发送消息到MQ
kafkaTemplate.send("order-created",
new OrderCreatedEvent(order.getId(), order.getUserId(), order.getAmount()));
}
}
/**
* 库存处理消费者
*/
@Service
public class InventoryConsumer {
@KafkaListener(topics = "order-created")
public void processOrderCreated(OrderCreatedEvent event) {
// 异步扣减库存
inventoryService.deductStock(event.getOrderId(), event.getItems());
}
}
/**
* 积分处理消费者
*/
@Service
public class PointsConsumer {
@KafkaListener(topics = "order-created")
public void processOrderCreated(OrderCreatedEvent event) {
// 异步增加积分
pointsService.addPoints(event.getUserId(), event.getAmount());
}
}
/**
* 消息队列配置
*/
@Configuration
@EnableKafka
public class KafkaConfig {
@Bean
public ProducerFactory<String, Object> producerFactory() {
Map<String, Object> props = new HashMap<>();
props.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "localhost:9092");
props.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class);
props.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, JsonSerializer.class);
// 高并发优化配置
props.put(ProducerConfig.BATCH_SIZE_CONFIG, 16384);
props.put(ProducerConfig.LINGER_MS_CONFIG, 10);
props.put(ProducerConfig.BUFFER_MEMORY_CONFIG, 33554432);
props.put(ProducerConfig.ACKS_CONFIG, "1");
props.put(ProducerConfig.MAX_IN_FLIGHT_REQUESTS_PER_CONNECTION, 5);
props.put(ProducerConfig.RETRIES_CONFIG, 3);
return new DefaultKafkaProducerFactory<>(props);
}
@Bean
public ConsumerFactory<String, Object> consumerFactory() {
Map<String, Object> props = new HashMap<>();
props.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "localhost:9092");
props.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringDeserializer.class);
props.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, JsonDeserializer.class);
props.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG, "order-service");
// 高并发优化配置
props.put(ConsumerConfig.FETCH_MIN_BYTES_CONFIG, 1024);
props.put(ConsumerConfig.FETCH_MAX_WAIT_MS_CONFIG, 500);
props.put(ConsumerConfig.MAX_POLL_RECORDS_CONFIG, 500);
return new DefaultKafkaConsumerFactory<>(props);
}
}
}
监控与弹性伸缩
系统监控体系
/**
* 高并发系统监控实现
*/
public class SystemMonitoring {
/**
* 指标收集与监控
*/
@Component
public class SystemMetrics {
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
// QPS监控
private final Counter requestCounter;
// 响应时间监控
private final Timer responseTimer;
// 错误率监控
private final Counter errorCounter;
public SystemMetrics(MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
this.requestCounter = Counter.builder("http.requests.total")
.description("Total HTTP requests")
.register(meterRegistry);
this.responseTimer = Timer.builder("http.request.duration")
.description("HTTP request duration")
.register(meterRegistry);
this.errorCounter = Counter.builder("http.errors.total")
.description("Total HTTP errors")
.register(meterRegistry);
}
public void recordRequest(String path, String method, long duration, boolean success) {
requestCounter.increment();
responseTimer.record(duration, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (!success) {
errorCounter.increment();
}
// 记录标签信息
meterRegistry.counter("http.requests",
"path", path,
"method", method,
"status", success ? "success" : "error"
).increment();
}
}
/**
* 弹性伸缩触发器
*/
@Component
public class AutoScalingTrigger {
private final KubernetesClient kubernetesClient;
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 30000) // 每30秒检查一次
public void checkScaling() {
double cpuUsage = getAverageCpuUsage();
double qps = getCurrentQPS();
double errorRate = getErrorRate();
if (shouldScaleUp(cpuUsage, qps, errorRate)) {
scaleUp();
} else if (shouldScaleDown(cpuUsage, qps, errorRate)) {
scaleDown();
}
}
private boolean shouldScaleUp(double cpuUsage, double qps, double errorRate) {
return cpuUsage > 0.7 || qps > 1000 || errorRate > 0.05;
}
private boolean shouldScaleDown(double cpuUsage, double qps, double errorRate) {
return cpuUsage < 0.3 && qps < 100 && errorRate < 0.01;
}
private void scaleUp() {
kubernetesClient.apps().deployments()
.inNamespace("default")
.withName("user-service")
.scale(Math.min(currentReplicas + 2, maxReplicas));
}
private void scaleDown() {
kubernetesClient.apps().deployments()
.inNamespace("default")
.withName("user-service")
.scale(Math.max(currentReplicas - 1, minReplicas));
}
}
}
总结
高并发系统设计是一个系统工程,需要从负载均衡、缓存架构、数据库分片、消息队列到监控弹性等多个层面进行综合考虑。负载均衡确保流量合理分配,多级缓存提升读取性能,分库分表解决数据存储瓶颈,消息队列实现异步解耦和流量削峰,完善的监控体系保障系统稳定运行。在实际项目中,需要根据业务特性和流量模式选择合适的架构方案,并通过持续的监控和优化来应对不断变化的并发挑战。


